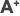EUROREGIONY W POLSCE - HISTORIA
EUROREGIONY NA GRANICACH POLSKI
Powstanie i funkcjonowanie euroregionów w Polsce
Mimo wielu wcześniejszych inicjatyw dotyczących współpracy regionów przygranicznych - np. w zakresie tzw. małego ruchu turystycznego, przygranicznej wymiany handlowej, transferu siły roboczej, kooperacji przemysłowej a także prób zagospodarowania Odry - w Polsce trwały wzrost możliwości współpracy transgranicznej obserwuje się od początku lat dziewięćdziesiątych, co ściśle wiąże się z transformacją ustrojową. W sferze praktycznej przejawia się to utworzeniem i funkcjonowaniem na granicach Polski 16 euroregionów.
Szczególne znaczenie dla powstających na granicy niemiecko-polskiej, a także polsko - czeskiej euroregionów miało powołanie w 1991 roku pierwszego na granicach Polski i w Europie Środkowej i Wschodniej Euroregionu Nysa". W latach 1991 - 1993 wypracował on w układzie trójstronnym pierwsze doświadczenia w tworzeniu podstaw instytucjonalnych współpracy transgranicznej. Euroregion Nysa, podobnie jak pozostałe 3 euroregiony na pograniczu zachodnim (Pomerania", Pro Europa Viadrina", i Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr"), ma modelowe znaczenie dla tworzenia różnych form współpracy ponadgranicznej na granicach Polski.
Regiony transgraniczne:
Wśród najważniejszych czynników sprzyjających powstawaniu regionów transgranicznych na granicy zachodniej należy przede wszystkim wymienić:
- nowy kształt polityczny granicy zachodniej, co spowodowało, że granica polsko-niemiecka stała się jednocześnie granicą zewnętrzną Unii Europejskiej,
- zawarcie układu stowarzyszeniowego Polski z Unią Europejską, co nadało polsko- niemieckiej współpracy transgranicznej charakter prekursorski w skali Europy Środkowej i Wschodniej,
- aktywność środowisk lokalnych i regionalnych w nawiązywaniu współpracy transgranicznej.
Także korzystne zmiany polityczne ostatnich lat stwarzają nowe możliwości dla zbliżenia i wzajemnej koordynacji rozwoju oraz odnowy powiązań międzyregionalnych i lokalnych na pograniczu południowym. Granica z Czechami i Słowacją stała się równocześnie granicą między państwami stowarzyszonymi z Unią Europejską. Jest to także granica wewnętrzna państw Grupy Wyszehradzkiej i granica wewnętrzna w ramach utworzonej przez to ugrupowanie Strefy Wolnego Handlu(CEFTA).
Na pograniczu wschodnim współpraca euroregionalna najbardziej zaawansowana jest z Ukrainą, czego efektem było powołanie we wrześniu 1995 roku pierwszego w Europie Wschodniej Euroregionu Bug.
Na pograniczu północnym pierwsze inicjatywy nadania form instytucjonalnych współpracy transgranicznej pojawiły się w 1997 roku. W wyniku intensywnych prac organizacyjnych środowisk lokalnych i regionalnych obszarów przygrani-nych państw nadbałtyckich, w lutym 1998 roku podpisano w Malborku umowę o utworzeniu Euroregionu Bałtyk, obejmującego przygraniczne obszary Polski, Danii, Litwy, Łotwy, Rosji (Obwód Kalingrad) i Szwecji.
Chronologia tworzenia euroregionów:
1 „Nysa" 21 grudnia 1991
2 „Karpacki" 14 lutego 1993
3 „Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr" 21 września 1993
4 „Pro Europa Viadrina" 21 grudnia 1993
5 „Tatry" 26 sierpnia 1994
6 „Bug" 29 września 1995
7 „Pomerania" 15 grudnia 1995
8 „Glacensis" 5 grudnia 1996
9 „Niemen" 6 czerwca 1997
10 „Pradziad" 2 lipca 1997
11 „Bałtyk" 22 lutego 1998
12 „Śląsk Cieszyński" 22 kwietnia 1998
13 „Silesia" 20 września 1998
14 „Beskidy” 18 luty 2000
15 „Puszcza Białowieska” maj 2002
16. „Euroregion Łyna-Ława" wrzesień 2003
EUROREGIONS WITHIN THE POLISH BODERS
The establishment and functioning of the Euro-regions in Poland
Despite many earlier initiatives on cooperation of border regions - eg. in the field of so-called little tourism, cross-border trade, the transfer of labor, industrial cooperation and the development of the Oder attempts - in Poland, sustainable growth possibilities for cross-border cooperation is observed since the early nineties, which is closely associated with the political transformation. In the sphere of practical manifests itself is the establishment and operation on the Polish borders, 16 Euroregions.
Of particular importance for emerging on the German-Polish border and the Polish - Czech Euroregion was the establishment in 1991 of the first on the Polish border and in Central and Eastern Europe Euroregion Neisse. "In the years 1991-1993 he developed the tripartite arrangement first experience in creating an institutional basis cross-border cooperation. Euroregion Neisse, like the other three Euro-regions on the border between the western (Pomerania, "Pro Europa Viadrina" and Spree-Neisse-Bober "), has the model significance for the creation of various forms of cross-border cooperation on the Polish border.
Among the most important factors that contribute to the formation of cross-border regions to the western border should first of all include:
- new political shape of the western border, which resulted in the Polish-German border has become the external border of the European Union,
- Polish the conclusion of the Association Agreement with the European Union, which gave the Polish-German border cooperation a pioneer in the scale of Central and Eastern Europe,
- activity of local communities and regional authorities in establishing cross-border cooperation.
Also preferred political changes of recent years offer new opportunities for rapprochement and mutual coordination of development and renewal of interregional and local authorities on the border south. The border with the Czech Republic and Slovakia became at the same time the border between the countries associated with the European Union. It is also the internal frontier of the Visegrad Group and the internal frontier within the framework established by the group Free Trade Area (CEFTA).
On the eastern border of cooperation Euroregional most advanced is Ukraine, which resulted in the appointment in September 1995 of the first in Eastern Europe Euroregion Bug.
On the northern border of the first initiatives to give institutional forms of cross-border cooperation emerged in 1997. As a result of intensive organizational work of local communities and regional areas przygrani-of the Baltic states, in February 1998 in Malbork signed an agreement to establish ERB, including border areas of Polish, Denmark, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia (circuit Kalingrad) and Sweden.
Creating Euroregions chronology:
1 „Nysa" 21 December 1991
2 „Karpacki" 14 February 1993
3 „Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr" 21 September 1993
4 „Pro Europa Viadrina" 21 December 1993
5 „Tatry" 26 August 1994
6 „Bug" 29 September 1995
7 „Pomerania" 15 December 1995
8 „Glacensis" 5 December 1996
9 „Niemen" 6 June 1997
10 „Pradziad" 2 July 1997
11 „Bałtyk" 22 February 1998
12 „Śląsk Cieszyński" 22 April 1998
13 „Silesia" 20 September 1998
14 „Beskidy” 18 February 2000
15 „Puszcza Białowieska” in May 2002
16. „Euroregion Łyna-Ława" September 2003
 KALENDARZ WYDARZEŃ
KALENDARZ WYDARZEŃ
Przejdź na podstronę ze szczegółowymi informacjami. »
| Marzec 2026 | ||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER

Strona wyraża jedynie poglądy autorów i nie może być utożsamiana z oficjalnym stanowiskiem Ministerstwa Spraw Zagranicznych RP